I know many of you lean, mean, workout machine Breaking Muscle readers could care less about body fat reduction. You’re already there. Your focus goes to your lift resistance amounts, improving training times, shoring up your exercise techniques, strategic planning to defeat your opponents, future competition preparation, and feeling good about your training. That’s how it should be.
What About Fat Loss?
But guess what? There is a large segment of the population who are only concerned about shedding their “love handles.” Yes, most of these people will admit they’re over-fat due to lack of physical activity and eating like it’s Thanksgiving day multiple times per week. If taken to task, most people don’t want to resemble an unshapely blob of protoplasm. They would rather look better, but they just don’t know where to start to achieve that goal. On top of this, we all exist in a society where a plethora of high-calorie and/or low nutritional value food exists. Wise decisions must be made by all, regardless of your goals.
Is it possible to eat your favorite foods, be happy, and attain your fitness goals simultaneously? Maybe. There are hundreds of diets and workout programs purportedly geared toward expunging body fat while enjoying your favorite foods. Many of them work, provided you actually adhere to their guidelines and remain disciplined with sensible calorie intake and exercise.
But here’s my advice if you are attempting to maximally lose body fat: maintain your blood sugar level between 70 mg/dl and 110 mg/dl. Do this, and all other factors being equal, you will burn more fat. Biologically, it comes down to your body’s innate ability to regulate two hormones – insulin and glucagon – relative to dietary intake.
How Insulin and Glucagon Affect Fat Storage
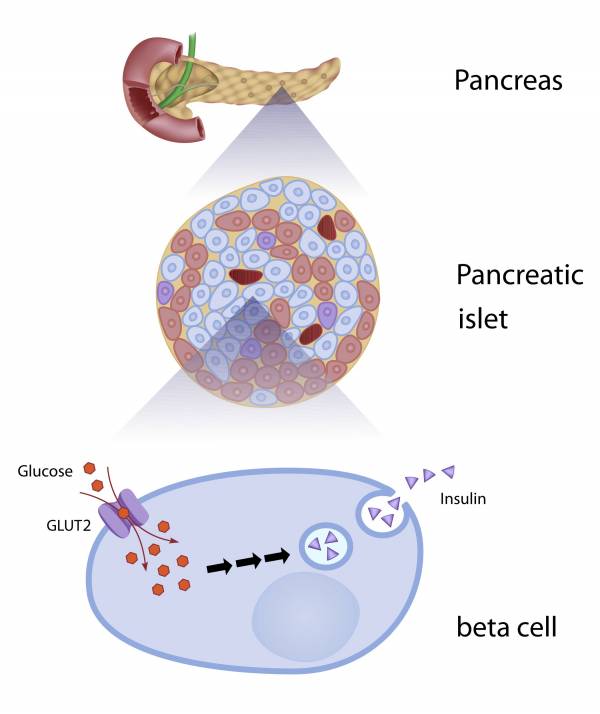 Insulin is secreted by the beta cells of the pancreas when your blood sugar levels are high. So, following a meal that contains mostly high glycemic, fast digesting carbohydrates, your blood sugar level may skyrocket well past the desired level of 110 mg/dl. This will facilitate storage of glucose (blood sugar) in the muscle tissues and especially fat cells.
Insulin is secreted by the beta cells of the pancreas when your blood sugar levels are high. So, following a meal that contains mostly high glycemic, fast digesting carbohydrates, your blood sugar level may skyrocket well past the desired level of 110 mg/dl. This will facilitate storage of glucose (blood sugar) in the muscle tissues and especially fat cells.
Glucagon is secreted by the alpha cells of the pancreas when blood sugar is low. This primarily occurs between feedings and when exercising. Glucagon causes the liver to release stored energy into circulation.
Essentially, insulin and glucagon work in balance – insulin increases, glucagon decreases, and vice versa. Insulin promotes storing energy and manufacturing proteins while glucagon promotes the release of stored energy, both glucose and fatty acids.
Simply put, keeping your blood glucose level in check (i.e., below 110 mg/dl) will cause your body to consistently burn more stored fat. A diet replete with good protein and carbohydrate sources will minimize insulin spikes, increase glucagon, and ultimately promote less fat storage, all other factors being equal.
So, to optimize fat reduction, it all gets back to what we’ve had pounded into our heads for years: eat properly and exercise sensibly. However, closer attention to the diet component to maintain an optimal blood sugar level can facilitate more fat burning throughout your day.
Photos courtesy of Shutterstock.






